In most consumer activities, the customer exchanges money for a product or quickly performed service. Auto insurance is different: The customer pays a fee to the insurance company, and the insurance company maybe provides a service or financial assistance at some point although if the service is never rendered, both the consumer and the company would probably be pleased. Auto insurance companies make money through a combination of managed risk and the strategic use of money. Insurers associate together large swaths of their policyholders into «groups» via the risk-assessment criteria discussed earlier — type of car, driving record, and so on. Out of each group, it’s likely that a very small percentage of these policyholders will endure a car accident severe enough to file a claim during the coverage period. That’s because managed risk spreads the short-term financial burden out over the rest of the group, the remaining members of which, in this scenario, haven’t received any payouts that cost the insurance company money. Further, insurance companies are essentially financial institutions: They take in money and dole out money, just like a bank does. Many insurance companies are even branches of large banking conglomerates.
How Auto Insurance Companies Make Money
To the casual observer, the life insurance industry can seem a bit mysterious. Yet — almost invariably, it seems — the carrier takes in enough income to make good on its promises and earn a nice profit. As one learns more about how the insurance works, this enigma starts to disappear. The reality is that the industry is more of a science than an art. By using statistics, providers are able to make educated assumptions about how much they should charge you in order to fulfill their obligations to both policyholders and shareholders. Companies also invest proceeds in various securities, which represent an additional source of earnings. The primary way that insurance firms make money is fairly simple — by taking in more money in premiums than they pay out in benefits. But how, exactly, can they do this reliably? And regardless of how long he lives, the insurer is on the hook for face value of the policy. Insurance firms resolve this problem by analyzing their entire pool of customers. For all they know, Customer Y might only live to age 40, which would probably mean taking a loss on his account. Actuaries are also responsible for making sure the company has sufficient capital reserves to cover unexpected events such as an abnormally high number of claims. Carriers also use statistics to identify the risk profile of certain customers prior to offering them a policy.
Sign-up now and stay updated on the latest money saving tips & trends
Other times, it enables them to price the policy in a way that correlates to their level of financial risk. Another key aspect of life insurance arithmetic is determining how many customers will continue paying their policies until death. Surprisingly, most individuals either allow their policy to lapse — in other words, they stop paying the premium — or surrender it to obtain the cash balance in their account. In the early days of the industry, virtually all of the premium income that carriers received came from life insurance or other lines of insurance that they sold. But since the s, annuity income has exceeded that of their bread and butter product.
Insurers are happy to break even on your policy if it means they get to keep all the returns from investing your premiums.
Why Zacks? Learn to Be a Better Investor. Forgot Password. Insurance companies invest in many areas, but most of all they invest in bonds.

Life Insurance 101
The concept that drives the insurance company revenue model is a business arrangement with an individual, company or organization where the insurer promises to pay a specific amount of money for a specific asset loss by the insured, usually by damage, illness, or in the case of life insurance, death. In return, the insurance company is paid regular usually monthly payments from its customer, for an insurance policy that covers life, home, auto, travel, business, and valuables, among other assets. Basically, the insurance contract is a promise by the insurance company to pay out for any losses to the insured across a variety of asset spectrums, in exchange for regular, smaller payments made by the insured to the insurance company. The promise is cemented in an insurance contract, signed by both the insurance company and the insured customer. That sounds easy enough, right? But when you get down to how insurance companies make money, i. Let’s clear the air and examine how insurance companies make money, and how and why their risk-based revenue has proven so profitable over the years. As an insurance company is a for-profit enterprise, it has to create an internal business model that collects more cash than it pays out to customers, while factoring in the costs of running their business. To do so, insurance companies build their business model on twin pillars — underwriting and investment income. Make no mistake, insurance company underwriters go to great lengths to make sure the financial math works in their favor. The entire life insurance underwriting process is very thorough to ensure a potential customer actually qualifies for an insurance policy. The applicant is vetted thoroughly and key metrics like health, age, annual income, gender, and even credit history are measured, with the goal of landing at a premium cost level where the insurance company gains maximum advantage from a risk point of view. That’s important, as the insurance company underwriting business model ensures that insurers stand a good chance of making additional income by not having to pay out on the policies they sell. Insurance companies work very hard on crunching the data and algorithms that indicate the risk of having to pay out on a specific policy.
That’s because managed risk spreads the short-term financial burden out over the rest of the group, the remaining members of which, in this scenario, haven’t received any payouts that cost the insurance company money. This means that the auto insurance company won’t pay for damages or medical bills beyond a specific amount that the driver agrees upon. Partner Links. Compare Investment Accounts. Out of each group, it’s likely that a very small percentage of these policyholders will endure a car accident severe enough to file a claim during the coverage period.
About The Author
This pays for damage to your car, or even the theft of the car if it is not recovered. For example, there is property coverage. In a basic annuity, the policyholder makes either a series of payments or a lump-sum installment and, at a pre-determined, starts receiving regular checks from the insurance carrier. The Bottom Line. Insurance firms resolve this problem by analyzing their entire pool of customers. Term Life Insurance Term life insurance is a type of life insurance that guarantees payment of a death benefit during a specified time period. This can be avoided if you simply pay a monthly, quarterly, biannually, or even annual premium for your automobile insurance.
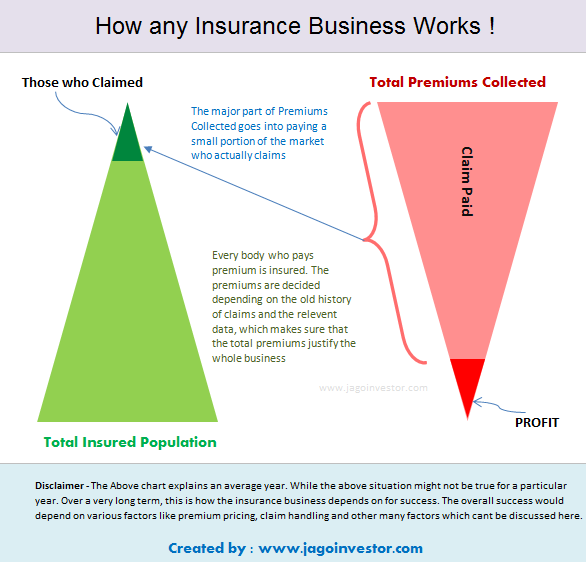
Insurance is about sharing risk. By distributing the risk of a catastrophe among a group of people, insurance offers a low-cost approach to providing financial security against unforeseen and, quite often, financially devastating events. Each insurance policy, then, is a contract or a promise between you and the insurance company. The contract stipulates that should you suffer a significant loss on, say, your car or house, the insurance company will cover that loss based upon the contract terms.
How Auto Insurance Companies Make Money
But in order for an insurance company to take on the risk of such a loss, policyholders must pay a fee, which is known as a premium. These premiums are used to pay for claims. To earn revenue insurance companies calculate the risk on each policy and set the premium accordingly. The difference between the premiums collected and the money paid out in insurance claims is known as underwriting income.
Comments
Post a Comment